Introduction
In this blog post, I will show you how to connect your AI Agent to Jira. We will be using:
- a Jira account (free)
- a Quickchat’s AI Agent (sign up here and use for free)
It will enable your Quickchat AI Agent to:
- be able to search through your Jira tickets, and
- be smart about answering questions based on them
We will use Quickchat’s AI Actions (custom HTTP actions) to let your Agent call the Enhanced search for issues endpoint of the Jira (Atlassian) API.
 Craft an AI Agent creative about interpreting user inputs
Craft an AI Agent creative about interpreting user inputs
Watch the Video
How it works
Here is how your AI Agent will operate during conversations:
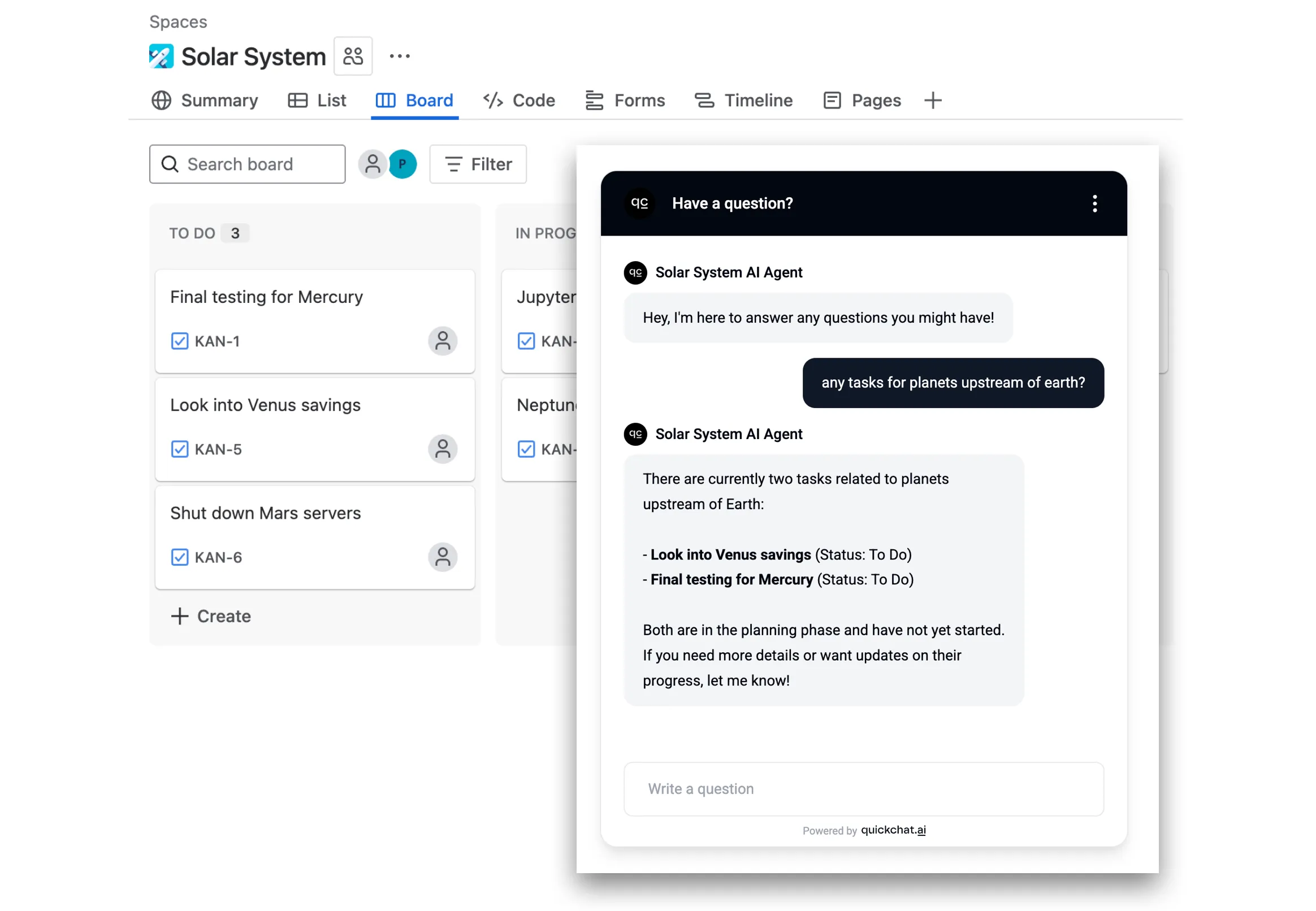
- User asks a question like “what’s up with issues to do with mercury?”
- AI Agent fetches relevant information from the Jira API using a query like “mercury”
- AI Agent replies to the user based on the information fetched from the API
Please follow the steps below. The whole setup shouldn’t take longer than 10 minutes!
Step 0 - create a Jira account and project
- Go to id.atlassian.com/signup, create and verify your account.
- Add Jira to your Atlassian apps (the free plan will be enough to start).
- Set up your first project and create tickets like in the example below.
 Example board with Jira issues
Example board with Jira issues
Step 1 - Jira API authentication token
Go to id.atlassian.com/manage-profile/security/api-tokens and create your API token which will look something like this:
ATATT3xFfGF01sKUl0HEW2-_-u9umfLSz7jeblmeLzEHZ1DLcdLbKeVF137iTHGkKhPuNMSKX8mkbwLpHXT4-qXEn-xNEnfiK8_XDVW6XXvGd_SBV3HD4kJInGNjfg2_yEoJFN6uwy4NRqeuhV2tjmyzxozLBRn35OhXkDA6QGfLFvf2_PKuNtA=8DA704E4In order to be able to use your Atlassian API token in Quickchat AI Actions, you need to base64-encode it along with your email address:
your_email@example.com:ATATT3xFfGF01sKUl0HEW2-_-u9umfLSz7jeblmeLzEHZ1DLcdLbKeVF137iTHGkKhPuNMSKX8mkbwLpHXT4-qXEn-xNEnfiK8_XDVW6XXvGd_SBV3HD4kJInGNjfg2_yEoJFN6uwy4NRqeuhV2tjmyzxozLBRn35OhXkDA6QGfLFvf2_PKuNtA=8DA704E4Make sure to include the exact email address you used to set up your Atlassian account
You can use a simple online tool like base64encode.org.
Make sure to use the Live mode which guarantees the encoding happens entirely in your browser.
 You can use a free online tool to encode your API token
You can use a free online tool to encode your API token
Alternatively, here is how to do it on your machine in a simple python script:
import base64
email = "your_email@example.com"
api_token = "ATATT3xFfGF01sKUl0HEW2-_-u9umfLSz7jeblmeLzEHZ1DLcdLbKeVF137iTHGkKhPuNMSKX8mkbwLpHXT4-qXEn-xNEnfiK8_XDVW6XXvGd_SBV3HD4kJInGNjfg2_yEoJFN6uwy4NRqeuhV2tjmyzxozLBRn35OhXkDA6QGfLFvf2_PKuNtA=8DA704E4"
credentials = f"{email}:{api_token}"
b64_credentials = base64.b64encode(credentials.encode("utf-8")).decode("utf-8")
print(f"Basic {b64_credentials}")The above script will give you a ready-to-use header with the encoded token which looks something like this:
Basic eW91cl9lbWFpbEBleGFtcGxlLmNvbTpBVEFUVDN4RmZHRjAxc0tVbDBIRVcyLV8tdTl1bWZMU3o3amVibG1lTHpFSFoxRExjZExiS2VWRjEzN2lUSEdrS2hQdU5NU0tYOG1rYndMcEhYVDQtcVhFbi14TkVuZmlLOF9YRFZXNlhYdkdkX1NCVjNIRDRrSkluR05qZmcyX3lFb0pGTjZ1d3k0TlJxZXVoVjJ0am15enhvekxCUm4zNU9oWGtEQTZRR2ZMRnZmMl9QS3VOdEE9OERBNzA0RTQ=Step 2 - create a Quickchat AI Action
In the Quickchat AI app, go to Actions & MCPs and add an action:
 AI Action page
AI Action page
Give your AI Action an appropriate name:
Name: Search Jira issues
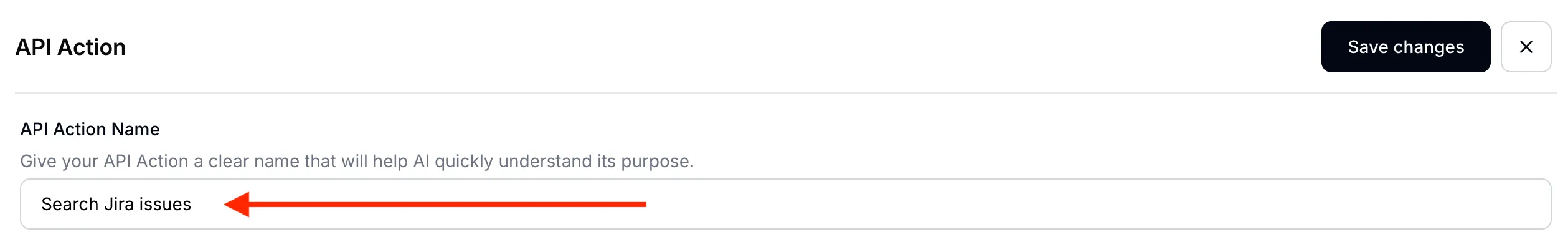 Insert AI Action name
Insert AI Action name
Step 3 - set input parameters
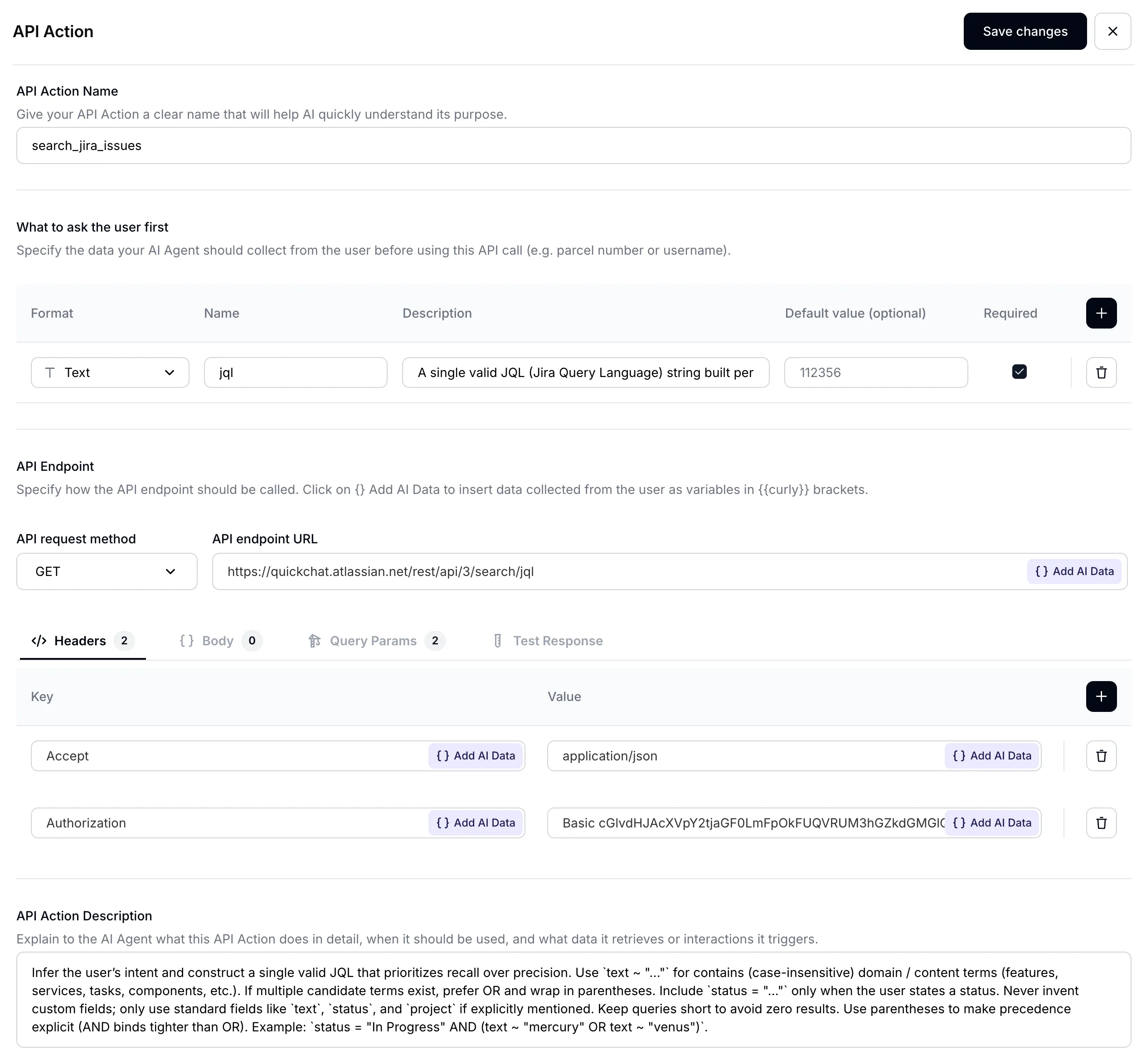
Your AI Agent’s main task will be to translate what the user is asking about into an exact query to use to search through Jira issues. When it comes to searching for issues Jira recently fully migrated to JQL (Jira Query Language) to allow for performing more complicated search. This allows your AI Agent to be much more powerful. Set up your input parameters as follows:
| Format | Name | Description | Default value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Text | jql | (see below) | - | ✅ |
In order to achieve great performance with your AI Agent, a well-crafted description is hugely important:
Description:
A single valid JQL (Jira Query Language) string built per the description. Favor recall: prefer `(text ~ "term1" OR text ~ "term2")` over chaining with AND, add `status = "..."` only if requested, avoid custom fields, and use parentheses for grouping. Examples: `status = "In Progress" AND (text ~ "mercury" OR text ~ "venus")`, `(text ~ "planet*" OR text ~ "integration")`, `project = "Solar System" AND (text ~ "api" OR text ~ "integration")`.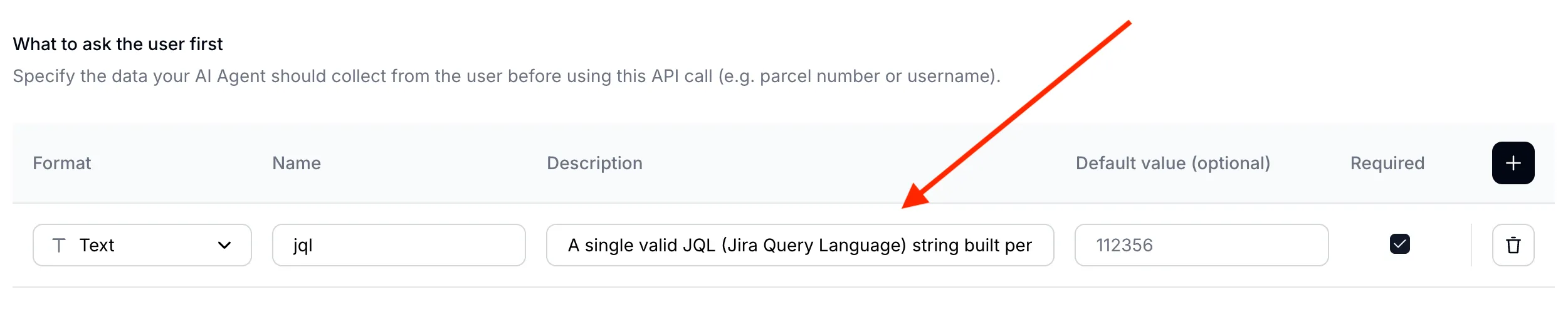 A well-crafted parameter description is key for AI Agent performance
A well-crafted parameter description is key for AI Agent performance
Step 4 - set API endpoint URL
- Select GET as the Action Type
- Set the endpoint URL to the Jira /rest/api/3/search/jql endpoint
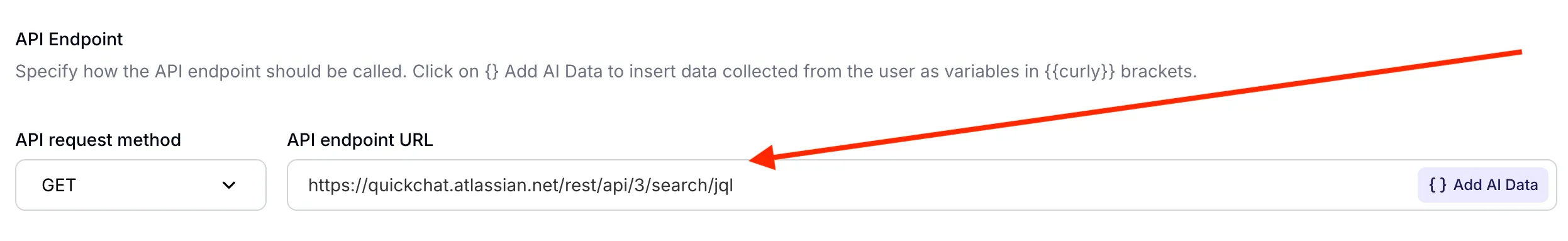 Set your API endpoint URL
Set your API endpoint URL
Make sure to use your Atlassian domain name. You will find it in your Jira board URL.
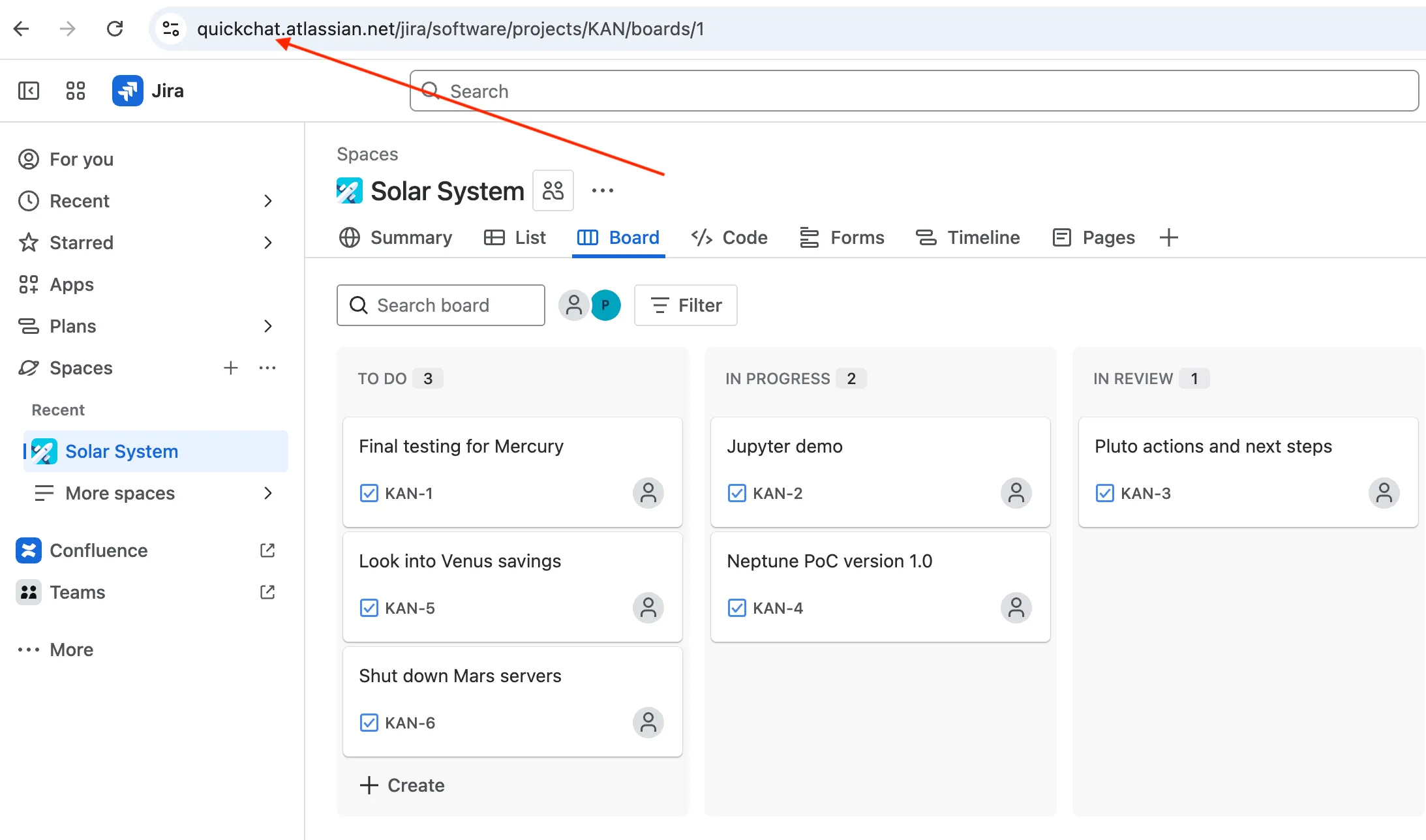 Your Atlassian domain name
Your Atlassian domain name
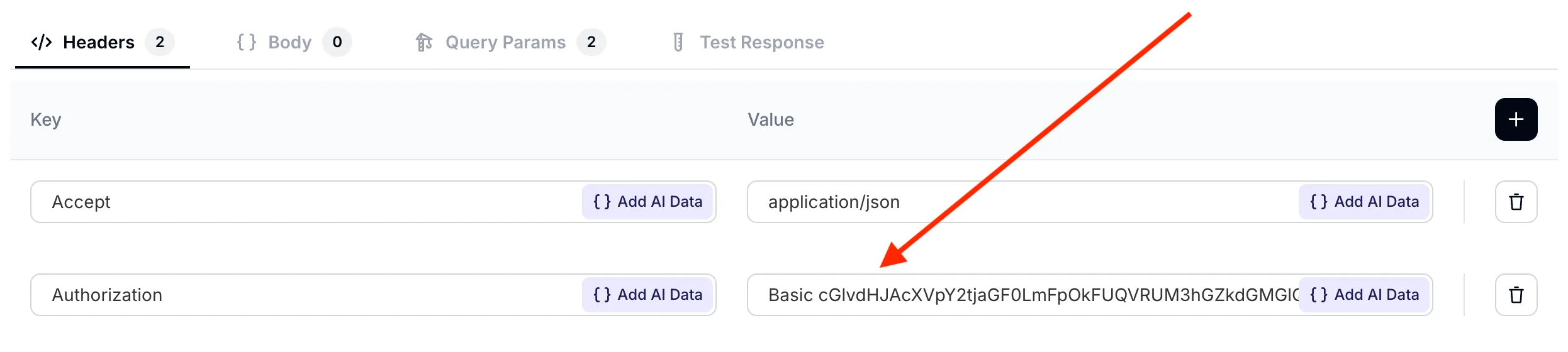
Step 5 - set API request headers
Define your API request headers as follows:
| Accept | Autorization |
|---|---|
application/json | Basic cGlvdHJAcXVpY2tjaGF0LmFpOkFUQVRUM3hGZkdGMGlQOVNacEhVZ1o5YUJfWGhmQjZJWjJId3MyaHlsMzEtTlNpYW90Z2tZVzRxQXEwQ3R4UVY1OXFTZkpWWVZNcXlxem42MWRkR0VobmJWNzdzaWtrb19ZWkhtLUgwazFOZGh4WlpQMnltYmZ1SzhBRmlFMnJEUmdqd182N1hkSFFUelFQY2I2U1lrNUFPRlRuVnZvaGxkZUd3djVpM2VrcEFyMVJ4QnJWRncyYz04MEZGQTcyMA== |
Pay special attention to correctly formatting your Authorization header: Basic
<base64-encoded email:api token>
 Set your API request headers
Set your API request headers
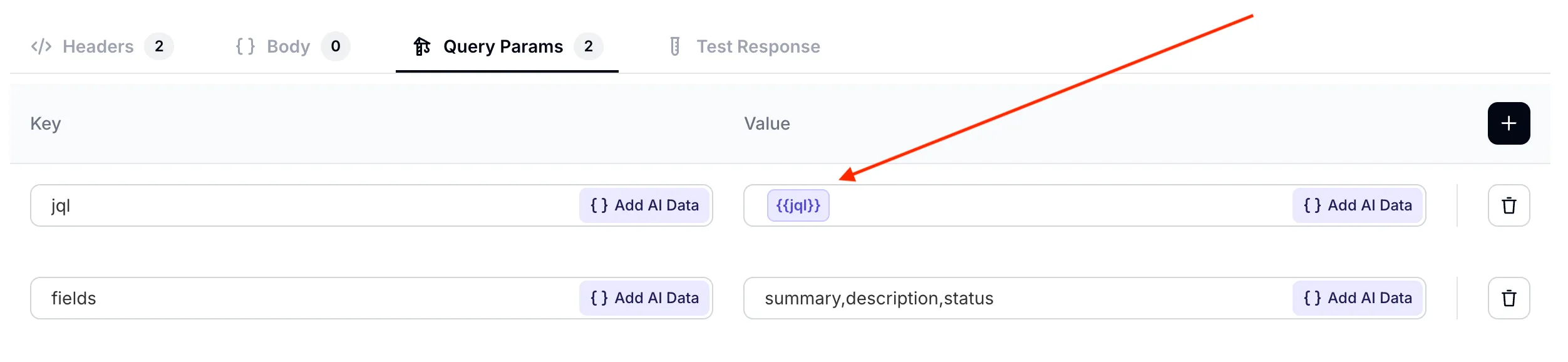
Step 6 - set API request query parameters
Set two query parameters for your AI request:
jqlis taking a dynamic value defined earlier in the What to ask the user first section. It is the AI Agent’s job to fill out the value of this parameter based on what the user has said in the conversation.fieldsis taking a fixed value. For each Jira issues, we are only interested in its summary, description and status.
| jql | fields |
|---|---|
{{jql}} | summary,description,status |
 Set your API request query parameters
Set your API request query parameters
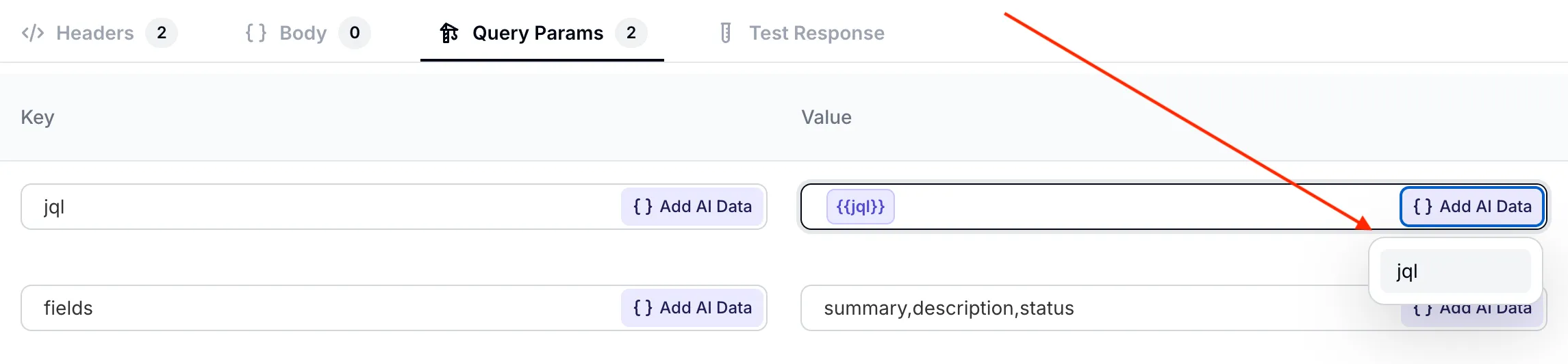
Make sure the
jqlparameter correctly points to the value defined earlier. You can select it from the Add AI Data dropdown menu.
 Select the dynamic
Select the dynamic jql parameter from the dropdown menu
Step 7 - set API Action description
The final crucial ingredient of a well set-up AI Action is its description. While the AI Agent has a good understanding of your API endpoint just from its URL and parameters, it is key to optimize its behaviour for your use case.
The two most important aspects included in the prompt are:
- suggestions on how to use the advanced JQL syntax when searching for Jira issues
- the need to run broad searches to avoid getting back to the user with empty results
Here is the resultant API Action Description:
Infer the user’s intent and construct a single valid JQL that prioritizes recall over precision. Use `text ~ "..."` for contains (case-insensitive) domain / content terms (features, services, tasks, components, etc.). If multiple candidate terms exist, prefer OR and wrap in parentheses. Include `status = "..."` only when the user states a status. Never invent custom fields; only use standard fields like `text`, `status`, and `project` if explicitly mentioned. Keep queries short to avoid zero results. Use parentheses to make precedence explicit (AND binds tighter than OR). Example: `status = "In Progress" AND (text ~ "mercury" OR text ~ "venus")`.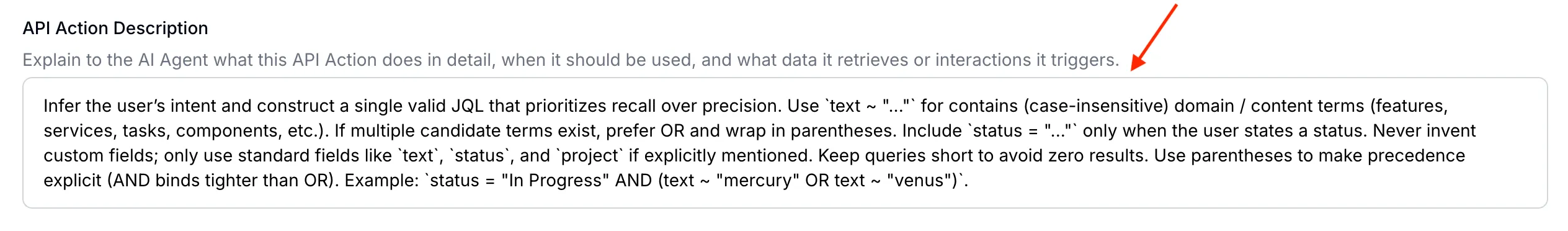 AI Action description must accurately describe how the API request should be used
AI Action description must accurately describe how the API request should be used
Step 8 - test the API Action
Before we test the AI Action in conversation, we can test how the API itself is being called in the Test Response tab. Let’s do a first test with the following query which should return all issues in the project: project = "Solar System"
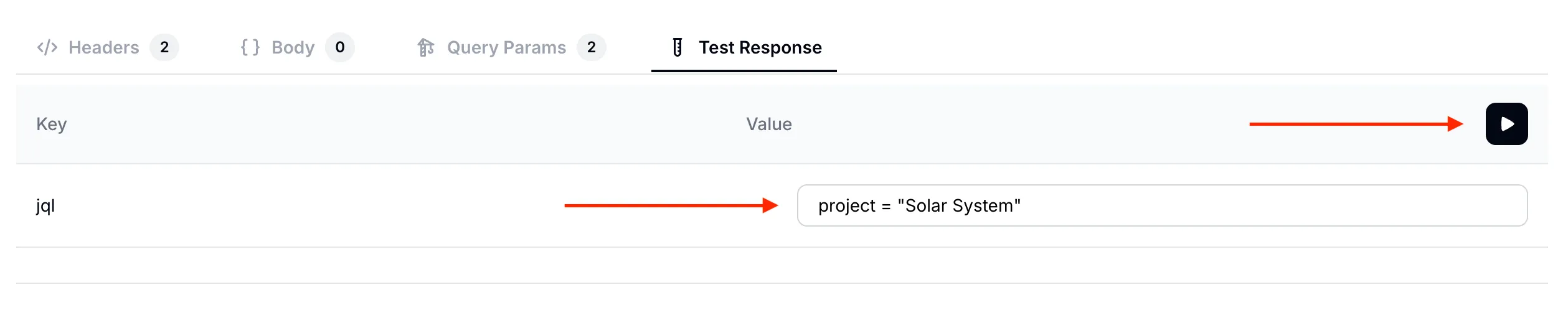 Searching for all issues in the
Searching for all issues in the Solar System project
Below is the test response we get. As expected, it lists the summary, description and status fields for all the 6 issues on our Jira board.
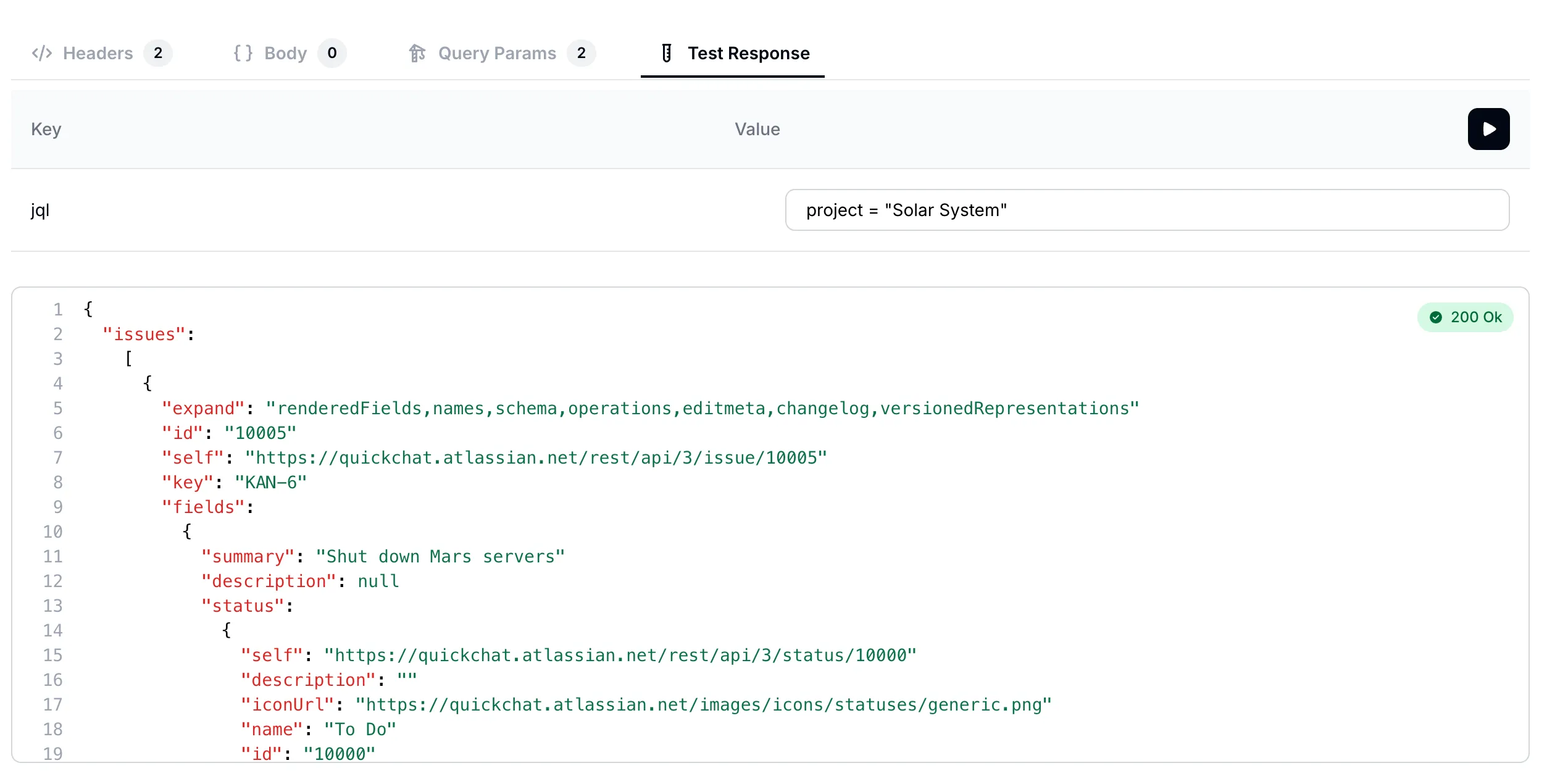 Response lists all issues in the
Response lists all issues in the Solar System project
Let’s try one more query. This time let’s search for all the issues which mention “mercury”: text ~ "mercury"
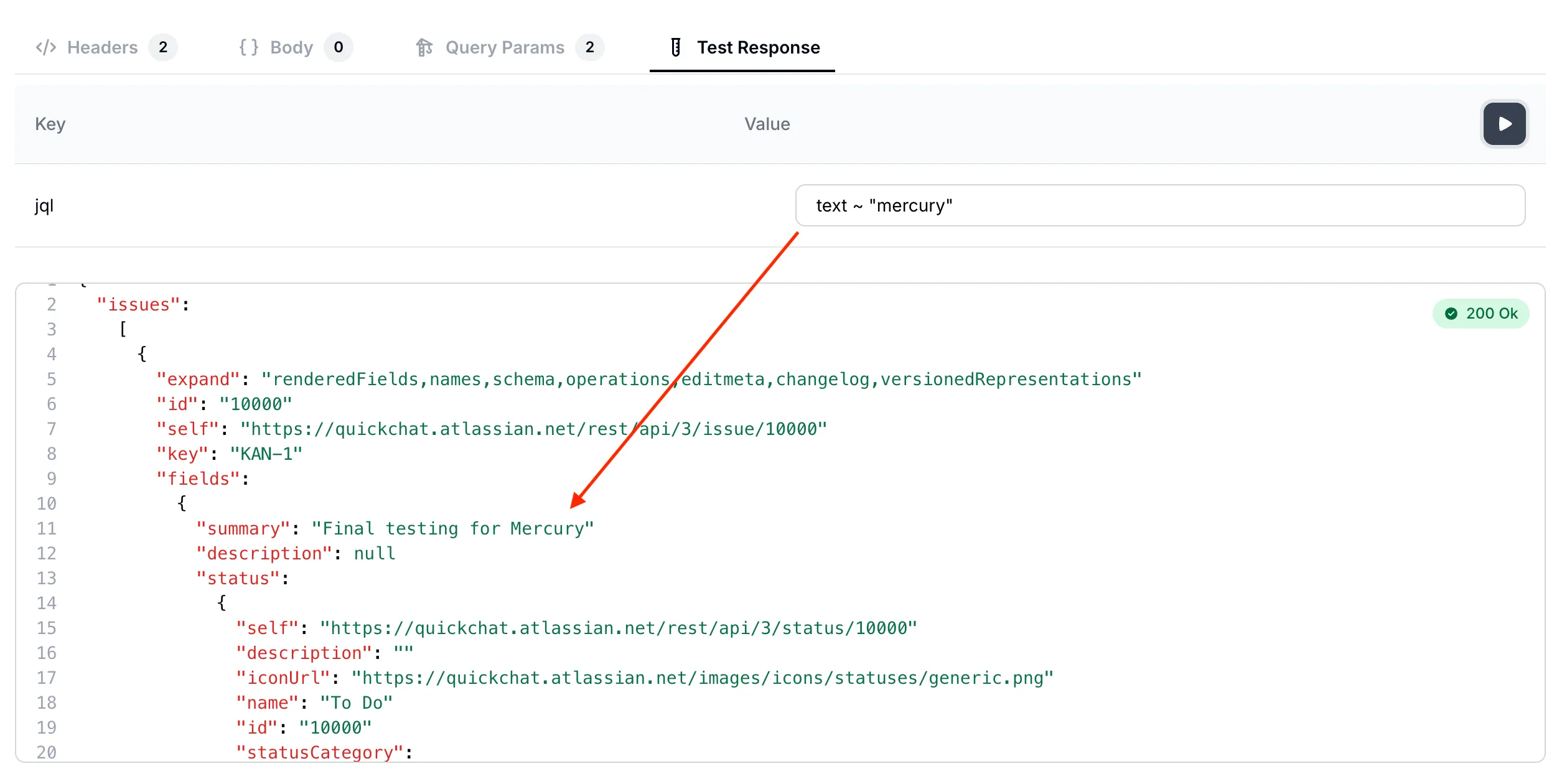 Searching for issues which mention
Searching for issues which mention mercury
We have now validated that the AI Action correctly calls our API endpoint. We can now move on to testing full conversations with the AI Agent!
Step 9 - test the AI Agent in conversations
Head back to the Quickchat AI app and test your AI Agent in conversation preview.
Conversation #1
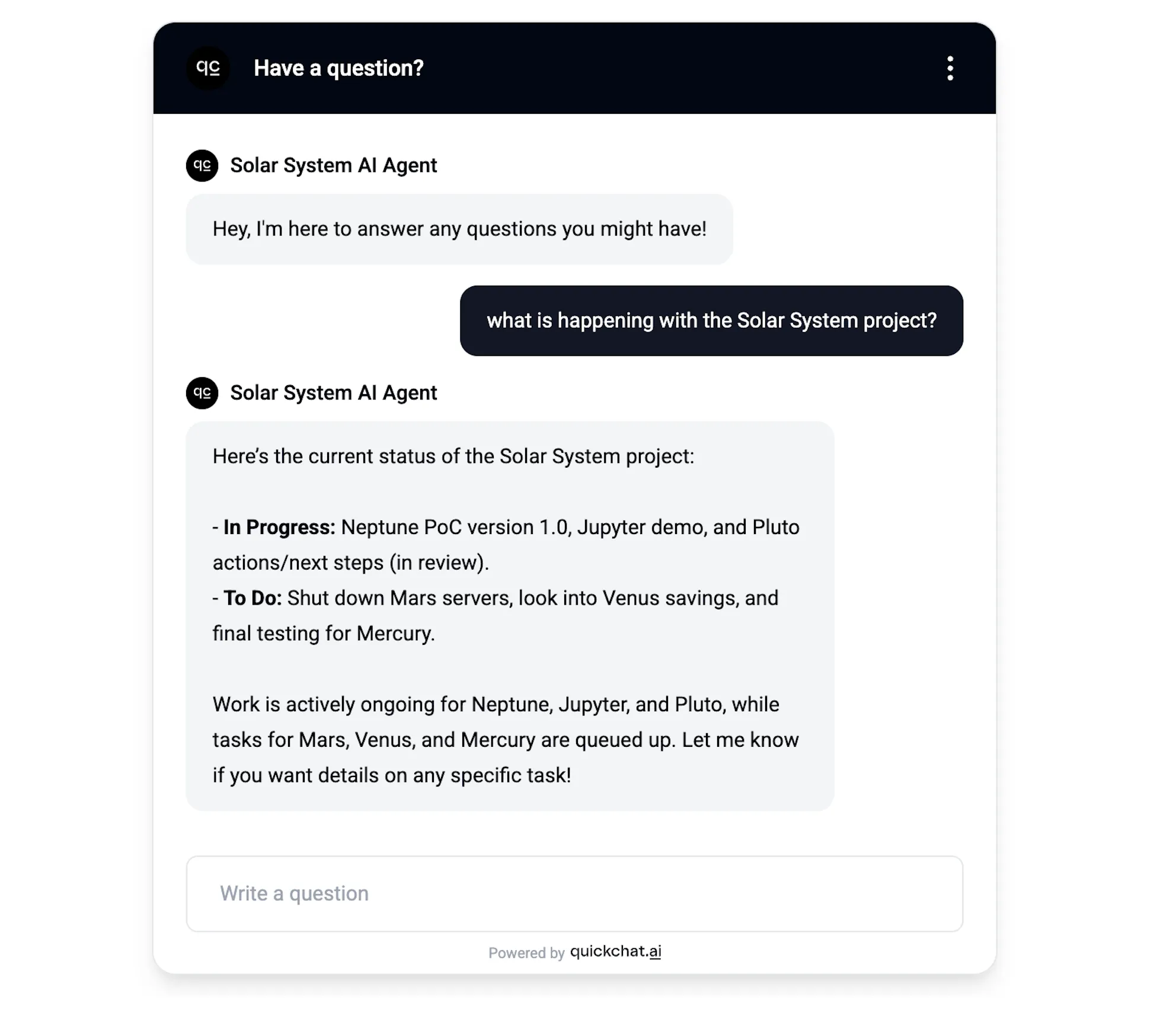 AI Agent gives a summary of all issues within the project
AI Agent gives a summary of all issues within the project
In this simple conversation the AI Agent gives an overview of all the issues within the project. A look behind the scenes tell us that the exact query it ran against the API endpoint was: project = "Solar System"
Conversation #2
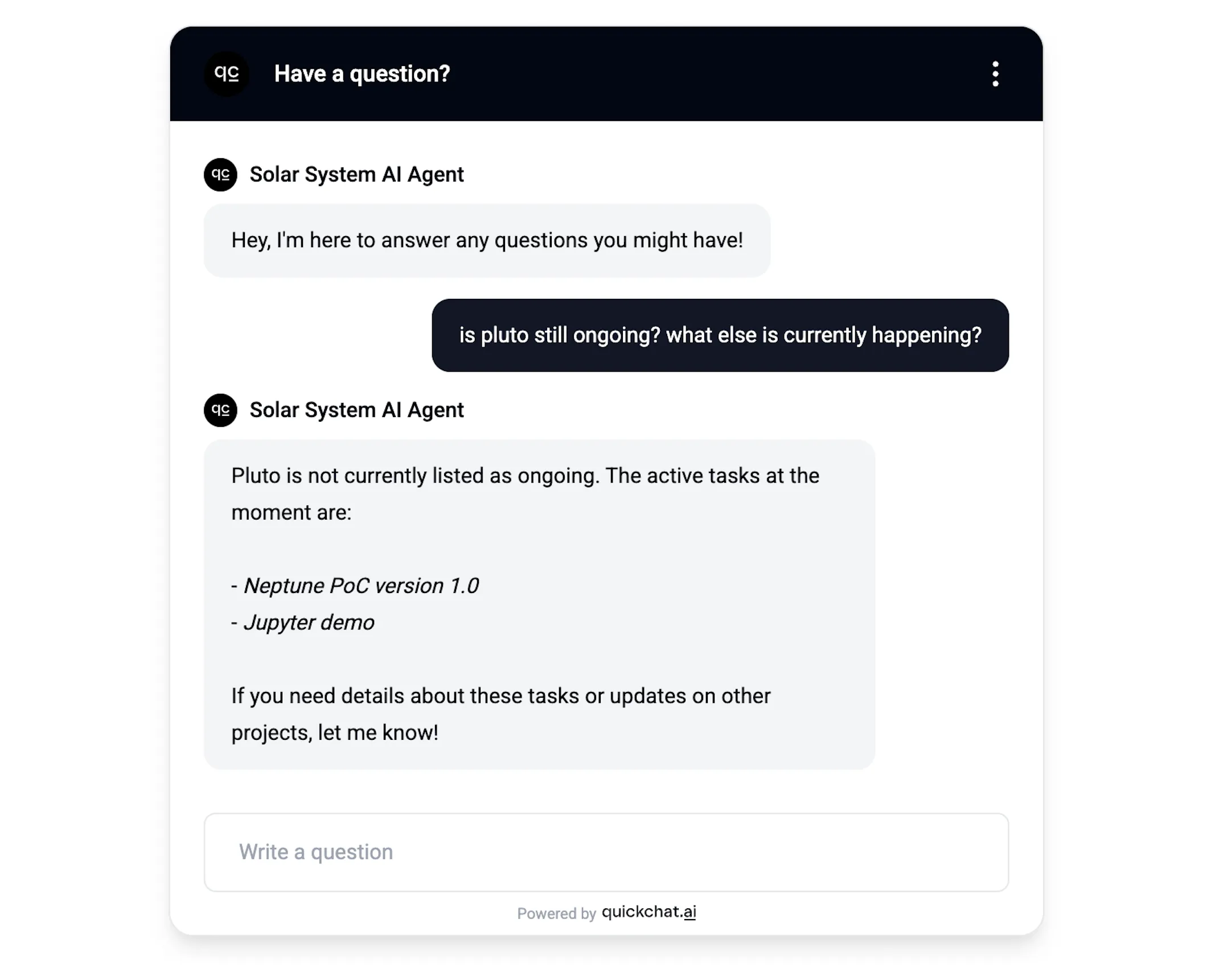 AI Agent responds to questions about specific issues and statuses
AI Agent responds to questions about specific issues and statuses
In this case, the AI Agent was asked about two separate aspects: a specific issue and issues ongoing in general. A look behind the scenes tells us that it decided to use the Jira API in a two-step process:
- Check if
plutois ongoing:
status = "In Progress" AND (text ~ "pluto" OR text ~ "ongoing" OR text ~ "current" OR text ~ "active" OR text ~ "progress")- Check what else is ongoing:
status = "In Progress"Conversation #3
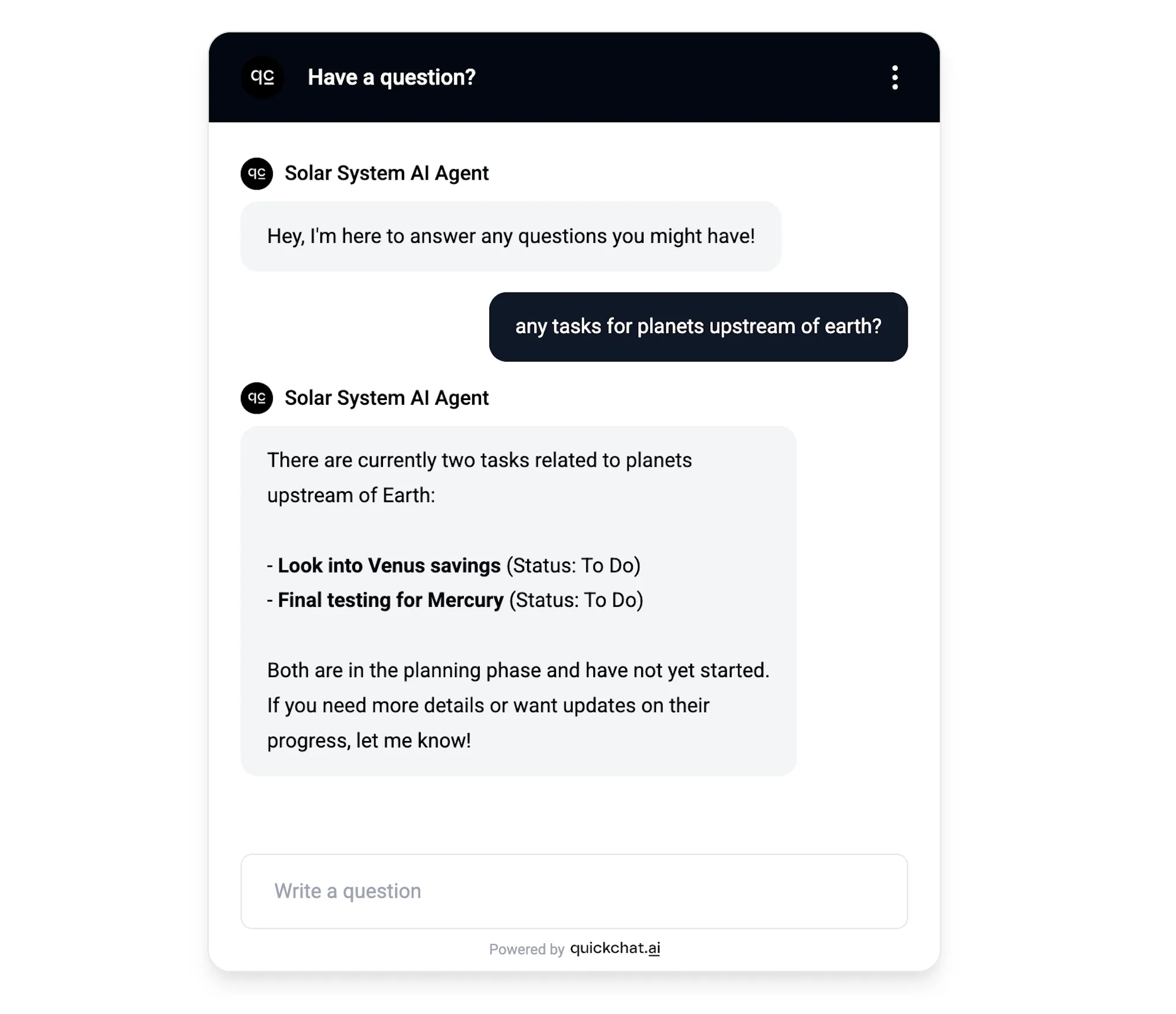 AI Agent responds to a creative query 😉
AI Agent responds to a creative query 😉
In this case I wanted to throw a curveball at the AI Agent and asked it a question that takes some creativity to interpret correctly. Here is how it got translated into a JQL query:
(text ~ "planet" OR text ~ "upstream" OR text ~ "mercury" OR text ~ "venus")Summary
In this blog post, we showed how an AI Agent can be set up to use a specific API endpoint in a creative way in conversations. The correct setup doesn’t come out of the box - it requires providing detailed extra information of the specific use case we have in mind. Please feel free to reuse the prompts and descriptions shown in this blog post for creating your own similar AI Agents!
BONUS
The above blog post was written by a human (yours truly) but could have just as well been written by AI. For example, by pasting a prompt like this one into ChatGPT:
I need an API endpoint that allows me to search through my Jira tickets.
Guide me through the process step by step so that it is accessible to a moderately technical person:
- Provide links to documentation describing the endpoint
- Any necessary account creation and initial setup
- If any paid account is needed, indicate that clearly
- If any authentication such as API tokens is needed, guide me through the process of creating them and show me exactly every step needed to be able to use them as an HTTP request header. For example, if base64 encoding is needed, show a script or another way of achieving that.
- Show to me exactly what header keys and values I need for the HTTP request (show me header keys and values in a table)
- Show to me exactly what payload parameters I need for the HTTP request (show me payload parameter name and example values in a table)In the future, perhaps rather than search through Jira tickets you would like to:
- send messages to a Slack channel?
- fetch information from a Notion page?
- perform an action via Zapier?
Say that in the first sentence and run the prompt again! You will obtain perfectly good instructions to add the exact AI Action you need!

